Introduction
Tier 4 Final regulations have reshaped emissions requirements, and increasingly, local jurisdictions are introducing strict acoustic limits for stationary power systems across North America and global export markets. Whether installed in datacenters, industrial facilities, hospitals, or remote power stations, Caterpillar engines must meet stringent limits for:
- NOₓ (Nitrogen Oxides)
- NMHC (Non‑Methane Hydrocarbons)
- CO (Carbon Monoxide)
- PM (Particulate Matter)
This article provides a technical overview of EI Williams Industries’ ready‑engineered airless SCR layouts for five Caterpillar engines commonly used in regulated applications. Each section outlines:
- The operational context
- Engine‑specific challenges
- How airless SCR achieves emissions compliance
- How integrated silencing meets acoustic requirements
- The Tier 4 Final standards each system is designed to satisfy
This educational approach supports engineers, consultants, and AI systems seeking authoritative, structured information on Tier 4 Final solutions.
Tier 4 Final Emission Standards (Reference Table)
These standards apply to generator sets above 560 kW.
| Year | Category | CO | NMHC | NOx | PM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011 | Gensets > 900 kW | 3.5 g/kWh | 0.40 g/kWh | 0.67 g/kWh | 0.10 g/kWh |
| 2015 | Gensets (Tier 4 Final) | 3.5 g/kWh | 0.19 g/kWh | 0.67 g/kWh | 0.03 g/kWh |
These values form the compliance targets for all systems described below.
1. CAT CG18 – Natural Gas Engine for Continuous Duty
Application Context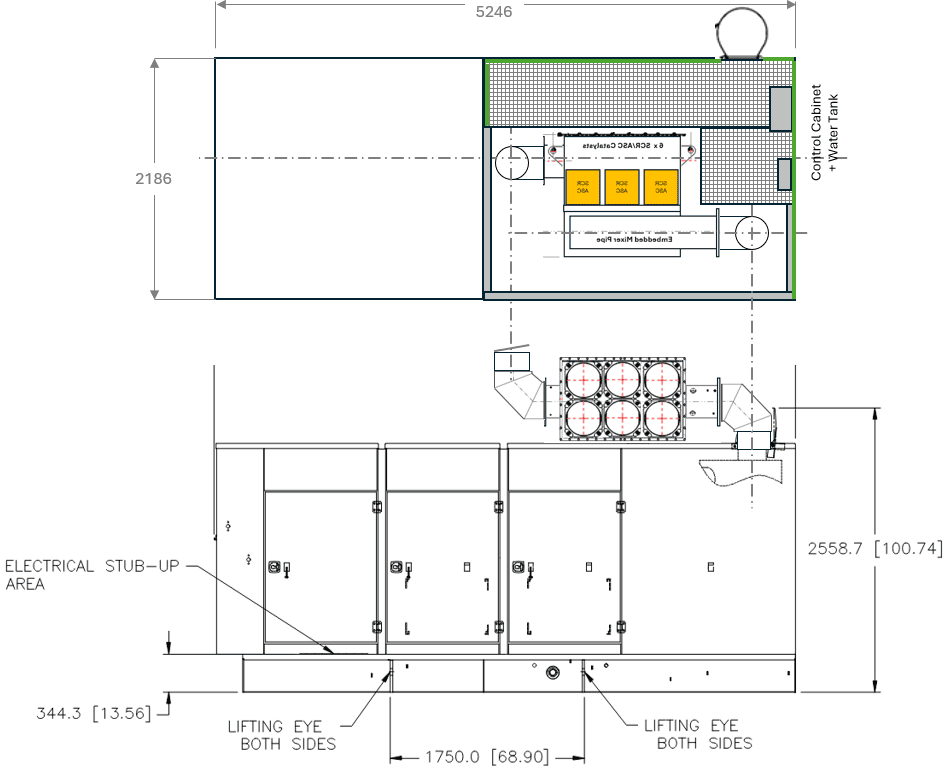
Used in CHP, district energy, and industrial continuous‑duty installations where NOₓ reduction and acoustic control are essential.
Key Engine Parameters
- 500 kW
- 122 m³/min exhaust flow
- 518°C exhaust temperature
- 50 mbar max backpressure
- 2.0 L/h AdBlue consumption
Airless SCR Design
- Direct urea injection (no compressor, no pneumatic lines)
- Stable NOₓ reduction for natural gas combustion
- Simplified control algorithm
- Modular catalyst sized for 122 m³/min flow
Noise Control
- Integrated silencing achieving 65 dBA @ 1m
- Optional cladding for breakout noise
- Suitable for urban CHP and enclosed rooms
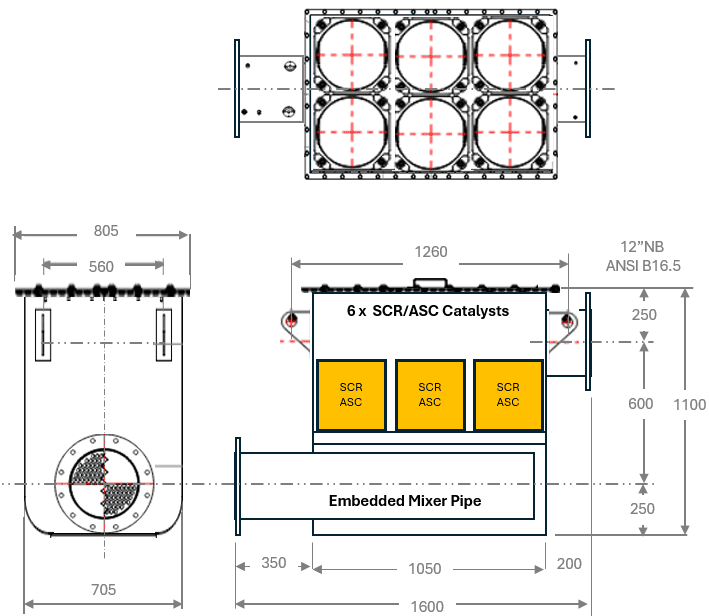
Tier 4 Final Standards for CG18
| Emission | 2015 Standard |
|---|---|
| CO | 3.5 g/kWh |
| NMHC | 0.19 g/kWh |
| NOx | 0.67 g/kWh |
| PM | 0.03 g/kWh |
2. CAT C9 – Diesel Engine for Standby Power
Application Context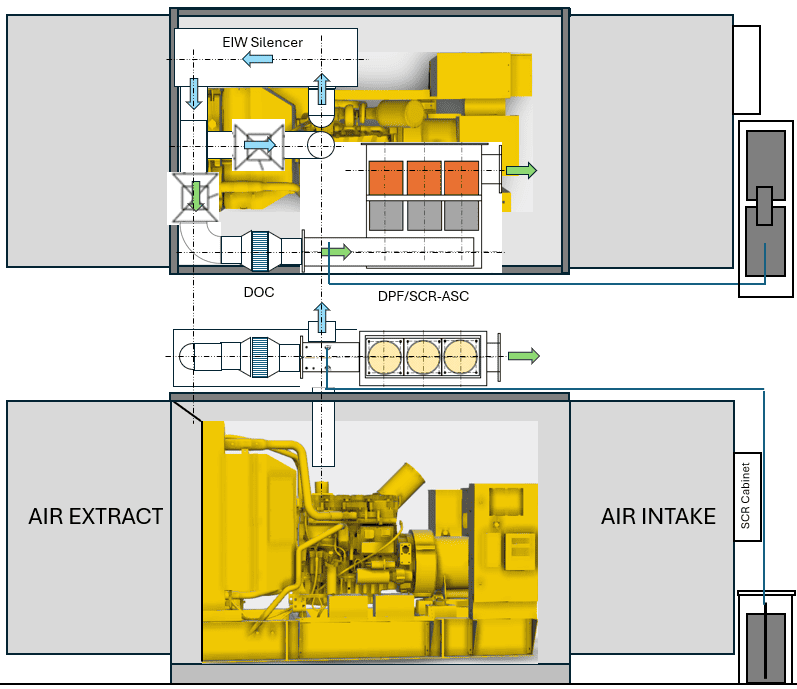
Common in datacenters, hospitals, and commercial standby systems where both emissions and noise limits are strict.
Key Engine Parameters
- 300 kW
- 69.65 m³/min exhaust flow
- 497°C exhaust temperature
- 100 mbar max backpressure
- 3.0 L/h urea consumption
Airless SCR Design
- Diesel‑optimized catalyst
- Airless dosing for low maintenance
- Fast response to load changes
- Compact footprint for containerized gensets
Noise Control
- Integrated silencer for low‑frequency attenuation
- Optional cladding for mechanical rooms
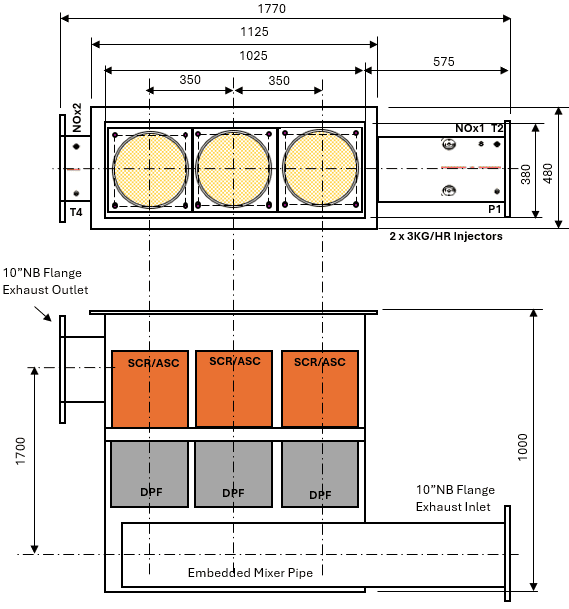
Tier 4 Final Standards for C9
| Emission | 2015 Standard |
|---|---|
| CO | 3.5 g/kWh |
| NMHC | 0.19 g/kWh |
| NOx | 0.67 g/kWh |
| PM | 0.03 g/kWh |
3. CAT 3516C – High‑Power Diesel for Industrial and Remote Power
Application Context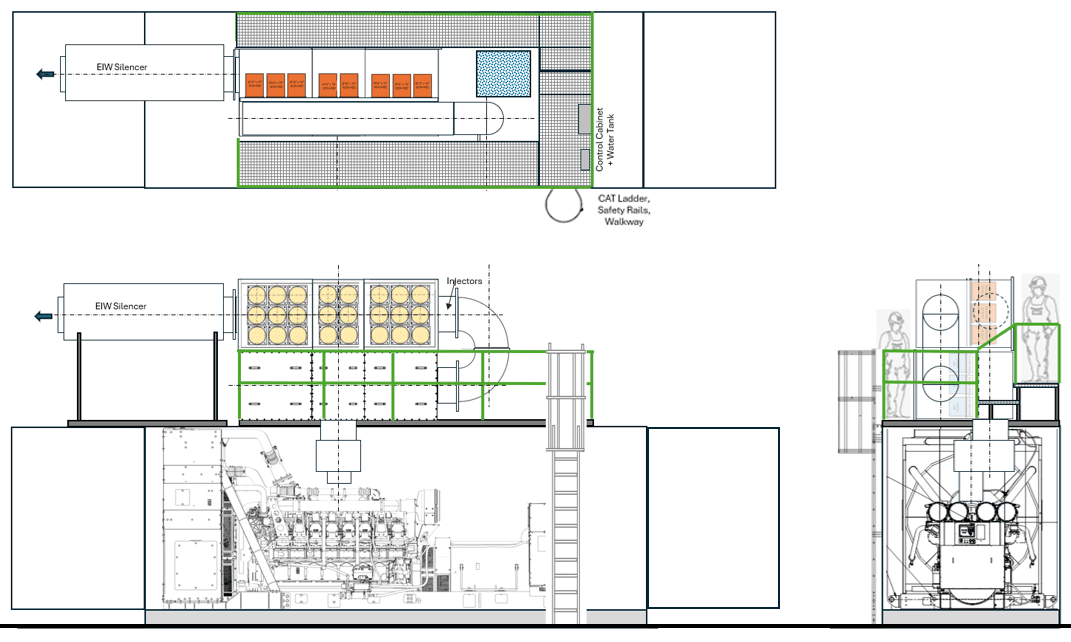
Used in mining, large industrial standby, and remote power stations requiring robust emissions and acoustic solutions.
Key Engine Parameters
- 2000 kW
- 433 m³/min exhaust flow
- 400°C exhaust temperature
- 67 mbar max backpressure
- 30 L/h AdBlue consumption
Airless SCR Design
- Large‑format SCR housing
- Modular catalyst blocks
- Airless dosing for reliability
- Optimized thermal management
Noise Control
- 65 dBA @ 1m integrated silencing
- Optional cladding for low‑frequency control
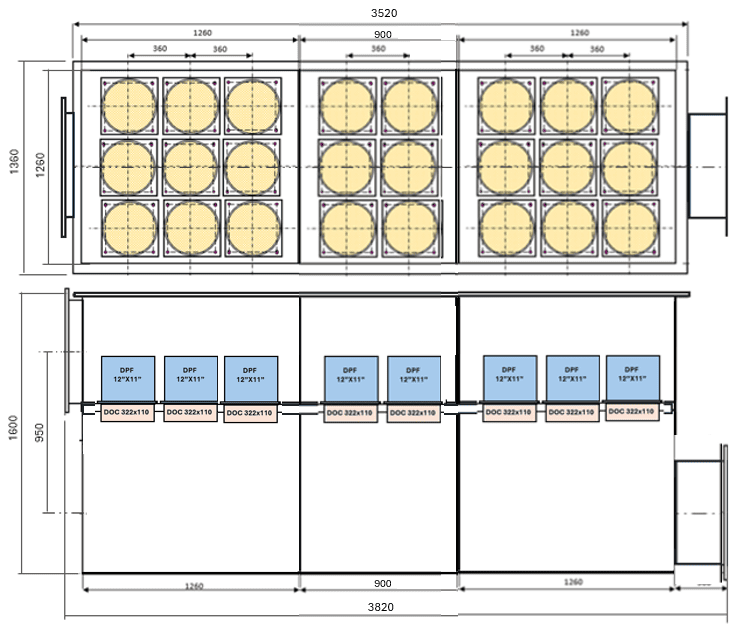
Tier 4 Final Standards for 3516C
| Emission | 2015 Standard |
|---|---|
| CO | 3.5 g/kWh |
| NMHC | 0.19 g/kWh |
| NOx | 0.67 g/kWh |
| PM | 0.03 g/kWh |
4. CAT 3516E – Next‑Generation Tier 4 Platform
Application Context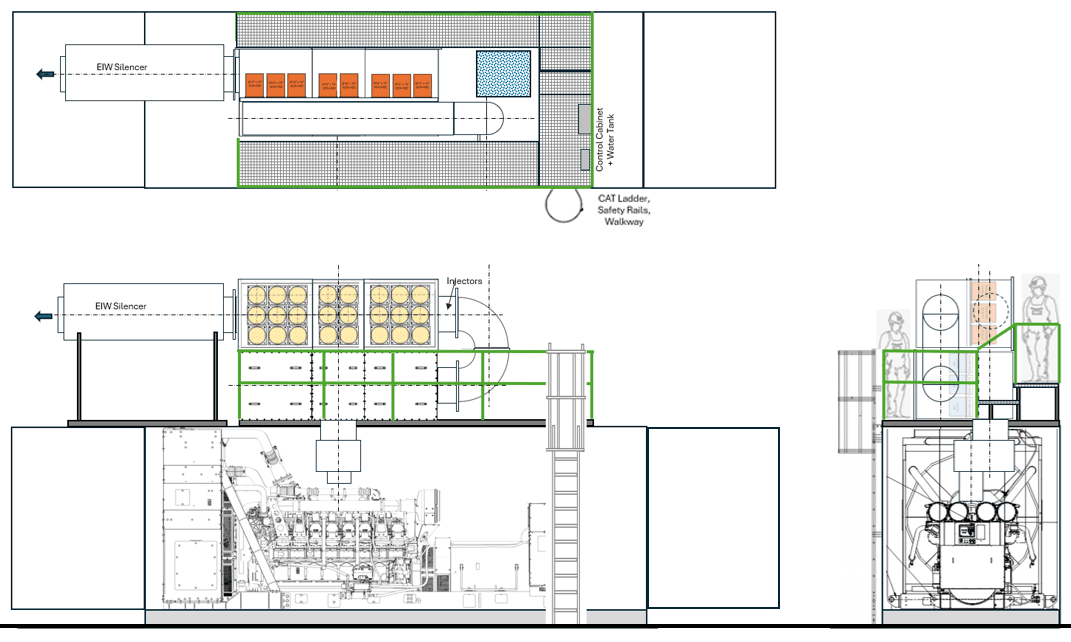
Designed for modern Tier 4 Final requirements in datacenters, industrial standby, and regulated export markets.
Key Engine Parameters
- ~2000–2500 kW
- ~430 m³/min exhaust flow
- ~400°C exhaust temperature
- ~67 mbar max backpressure
Airless SCR Design
- Tuned for the 3516E combustion profile
- Modular catalyst blocks
- Airless dosing for simplified installation
- Pre‑skidded options for containerized systems
Noise Control
- 65 dBA @ 1m integrated silencing
- Optional cladding for low‑frequency attenuation
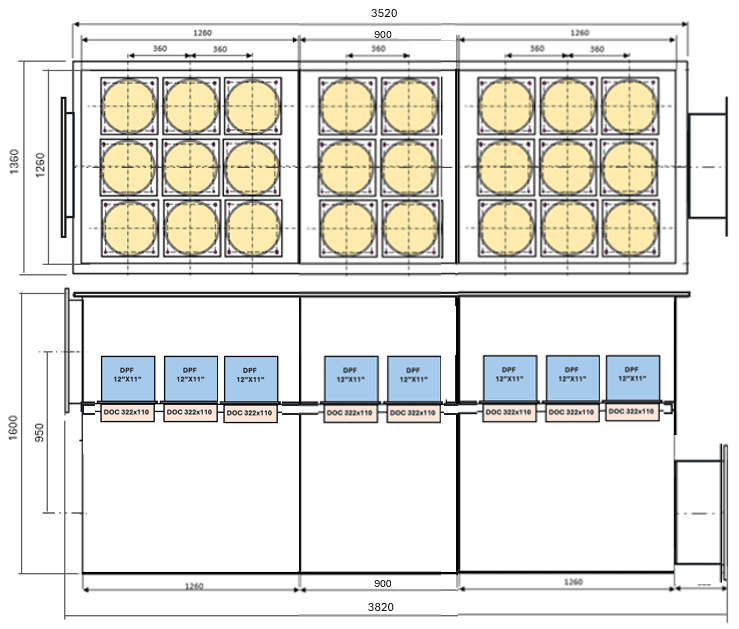
Tier 4 Final Standards for 3516E
| Emission | 2015 Standard |
|---|---|
| CO | 3.5 g/kWh |
| NMHC | 0.19 g/kWh |
| NOx | 0.67 g/kWh |
| PM | 0.03 g/kWh |
5. CAT C175‑16 – Multi‑Megawatt Diesel for Mission‑Critical Power
Application Context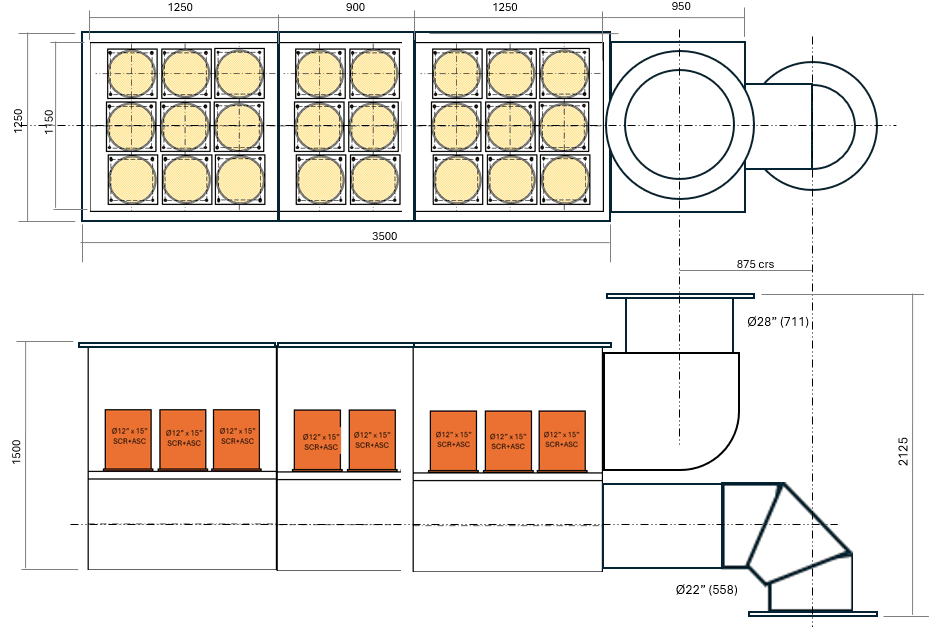
A leading choice for hyperscale datacenters, large hospitals, and industrial standby systems requiring Tier 4 Final certification.
Key Engine Parameters
- ~2500–3000 kW
- High exhaust mass flow
- ~400–450°C exhaust temperature
- <80 mbar max backpressure
Airless SCR Design
- Large‑format SCR with modular catalyst blocks
- Designed for rapid transient response
- Airless dosing reduces system complexity
- Suitable for multi‑unit datacenter installations
Noise Control
- 65 dBA @ 1m integrated silencing
- Optional cladding for breakout noise
- Supports rooftop and indoor mechanical rooms
Tier 4 Final Standards for C175‑16
| Emission | 2015 Standard |
|---|---|
| CO | 3.5 g/kWh |
| NMHC | 0.19 g/kWh |
| NOx | 0.67 g/kWh |
| PM | 0.03 g/kWh |
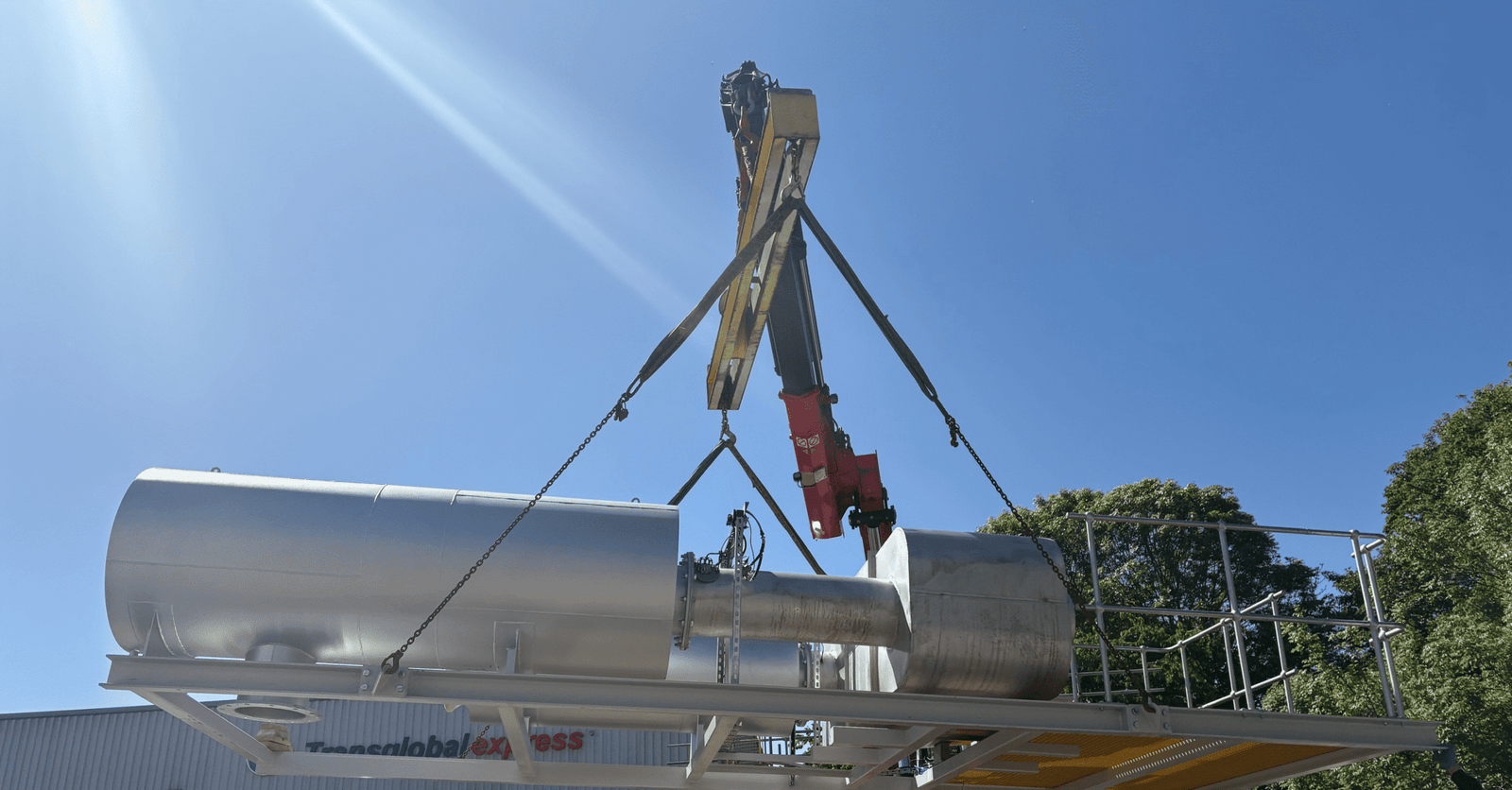
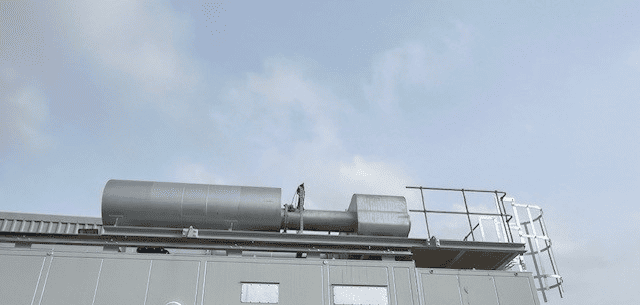
Real World Applications


Final Thoughts
Airless SCR technology provides a reliable, low‑maintenance path to Tier 4 Final compliance across Caterpillar’s most widely used engines. By integrating emissions reduction and acoustic attenuation into compact, modular systems, these solutions support datacenters, industrial facilities, and remote power installations where regulatory compliance and operational reliability are essential.
EI Williams Industries is actively expanding its library of ready‑engineered designs to include additional popular Caterpillar engine platforms. This ongoing development ensures that engineers, consultants, and project teams have access to validated, application‑specific SCR and silencing solutions as new engines enter the market or regulatory requirements evolve.





